Configurable 3D-Printed millifluidic and microfluidic ‘lab on a chip’ reactionware devices†
Abstract
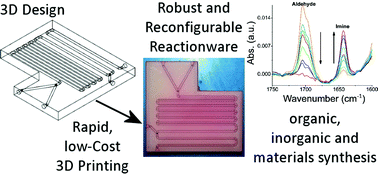
We utilise 3D design and 3D printing techniques to fabricate a number of miniaturised fluidic ‘reactionware’ devices for chemical syntheses in just a few hours, using inexpensive materials producing reliable and robust reactors. Both two and three inlet reactors could be assembled, as well as one-inlet devices with reactant ‘silos’ allowing the introduction of reactants during the fabrication process of the device. To demonstrate the utility and versatility of these devices organic (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...