Microfluidic one-step fabrication of radiopaque alginate microgels with in situ synthesized barium sulfate nanoparticles
Abstract
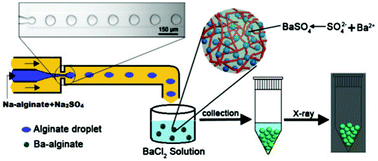
In this work, we report a new strategy to fabricate monodispersed radiopaque alginate (Ba–alginate) microgels by a one-step microfluidic method. Alginate droplets containing

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...