Blood plasma separation in a long two-phase plug flowing through disposable tubing†
Abstract
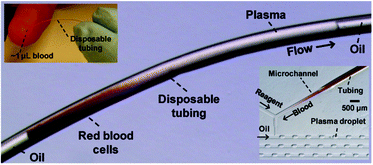
We report a simple technique to separate plasma from blood in a flowing immiscible plug. We investigate the effect of various control parameters such as blood dilution, injection flow rate, observation time and fluid properties on plasma separation. We find that the technique works best for diluted blood samples at low plug velocities and long observation times. We postulate that the main mechanism responsible for efficient separation is the sedimentation of blood cells in the plug and their subsequent collection by the moving plug causing a significant accumulation of cells at the rear of the plug. We discuss the time scales determining the sedimentation, advection and collection of a blood cell in the immiscible plug and propose a phase diagram that is able to predict the operating space for effective plasma separation. We demonstrate that the technique allows for the extraction of more than 60% of the plasma by volume from 1 μL of diluted blood. We show the practical significance of this method by compartmentalizing the separated plasma into discrete microfluidic droplets and detecting

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...