Separation of two phenotypically similar cell types via a single common marker in microfluidic channels†
Abstract
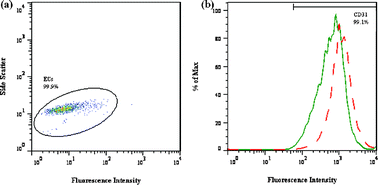
To isolate clinically and biologically relevant cell types from a heterogeneous population, fluorescent or magnetic tagging together with knowledge of surface

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...