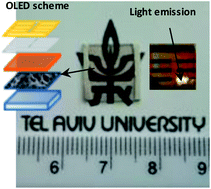
The next generation of optoelectronic devices requires transparent conductive electrodes to be flexible, cheap, and compatible with large scale manufacturing processes. Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) electrodes are often used due to their superior transparency and conductance, however they are brittle, expensive and their fabrication requires vacuum conditions which restrict scale-up. One possible alternative to the traditional ITO electrode is the metal nanowire mesh (MNWM) electrode, which is transparent, conductive, flexible and easy to produce. In this work we present the preparation and characterization of a simple organic light emitting diode (OLED) device based on a transparent electrode made of ultrathin MNWM and a comparison to an ITO based device. We have found that MNWM electrodes offer a suitable alternative to ITO electrodes in OLED devices. We have also found that the failure rate for devices due to short circuits between the top and bottom electrodes was smaller in MNWM based devices compared to ITO based devices since the MNWM devices could be repaired to present normal OLED behavior by selectively burning the nanowires forming the short. The ability to “heal” organic devices presents an important advantage and also allows for future uses in applications such as roll to roll printing.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...