Reducing hydrated protons co-intercalation to enhance cycling stability of CuV2O5 nanobelts: a new anode material for aqueous lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
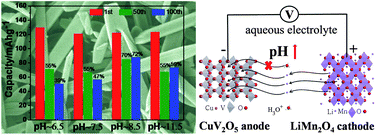
The aqueous-based lithium ion batteries have attracted considerable interest because of their high safety, low cost and environmental friendliness for rechargeable energy storage. Herein, a new anode material, uniform CuV2O5 nanobelts, was prepared through a facile hydrothermal route for the first time. The detailed structures and chemical state of the as-obtained CuV2O5 were investigated and the formation mechanism was proposed. The CuV2O5 nanobelts show high electrical conductivity, which could improve their Li-ion insertion/

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...