Zn-doped TiO2 electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells for enhanced photocurrent†
Abstract
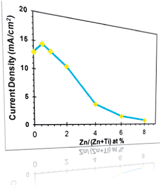
Porous nanocrystalline Zn/TiO2 materials were synthesized employing agarose gel as a template, achieving a maximum Zn-doping concentration of around 2 at.%. Low Zn-doping concentrations (e.g. <1 at.%) improved the photocurrent of the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...