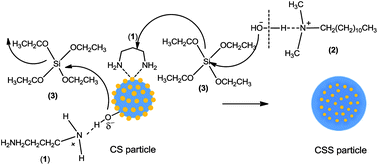
We report here (i) a method for the synthesis of highly monodisperse silica@gold@silica core–shell–shell (CSS) particles (<6% deviation in size) with coherent outer silica shells of directly tunable thickness and porosity, (ii) the fabrication of three unit cell thick (12 layers) metallodielectric photonic crystals (MDPCs) from these particles and (iii) their angle-resolved optical reflectance properties demonstrating the influence of dielectric contrast modification and metal plasmonic modes on photonic band gap properties. The synthetic route presented describes the use of two alkylamines, the first, 1,3-diaminopropane (DAP), as a surface manipulating agent, and the second, N,N-dimethyldodecylamine (DMDDA), as a catalyst for the outer silica shell formation, for the reproducible synthesis of monodisperse CSS particles avoiding the formation of the unwanted side-products such as core-free silica particles and aggregated particles with multiple cores. A rational chemical reaction mechanism describing the pathways involved in the formation of coherent silica shells, demonstrating the roles of both the amines, is proposed. The creation of partial wetting/de-wetting sites on gold nanoparticle surfaces by the adsorbed DAP molecules, the surface silanol modification by DAP and the slow hydrolysis–condensation reactions catalyzed by DMDDA are found to be responsible for the selective deposition of silica (heterogeneous nucleation) only onto the existing silica@gold core–shell particles leading to the formation of monodisperse CSS particles. The optical reflectance of the MDPC formed from these CSS particles shows an angle-dependent blue-shift that perfectly obeys the Bragg–Snell law predictions for photonic crystals. The dielectric contrast modification and the possible metal plasmonic mode-coupling in the MDPC also result in a high gap-to-midgap ratio (23%) as compared to the PC made of neat silica particles of comparable size (9%).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...