Chemistry, structure and processability of boron-modified polysilazanes as tailored precursors of ceramic fibers†
Abstract
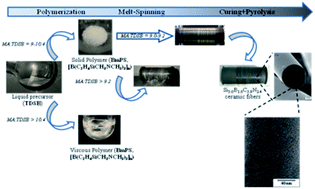
A series of boron-modified polysilazanes (BmPSs) of the type [B(C2H4SiCH3NCH3)3]n was synthesized by reaction of
* Corresponding authors
a
Institut Européen des Membranes (UMR CNRS 5635), IEM/Université Montpellier 2, CC047—Place E. Bataillon, 34095 Montpellier Cedex 5, France
E-mail:
Samuel.Bernard@iemm.univ-montp2.fr
b Laboratoire de Chimie de la Matière Condensée UMR CNRS 7574, UPMC Univ Paris 06, Collège de France, 11 Place M. Berthelot, 75005 Paris, France
c University of Bayreuth, 95440 Bayreuth, Germany
d H. C. Starck GmbH, Im Schleeke 78-91, D-38642 Goslar, Germany
e REOROM Laboratory, Hydraulics Department, “Politehnica” University of Bucharest, Splaiul Independentei 313, 060042 Bucharest, Romania
A series of boron-modified polysilazanes (BmPSs) of the type [B(C2H4SiCH3NCH3)3]n was synthesized by reaction of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
L. Gottardo, S. Bernard, C. Gervais, K. Inzenhofer, G. Motz, M. Weinmann, C. Balan and P. Miele, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 7739 DOI: 10.1039/C2JM15919H
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
