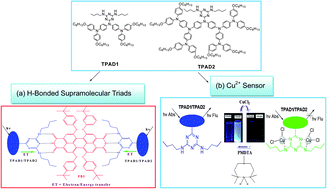
Two novel highly soluble triarylamine dendrimers TPAD1 and TPAD2 with N4,N6-dibutyl-1,3,5-triazine-4,6-diamine probe were synthesized via normal synthetic routes. Both dendrimers (TPAD1 and TPAD2) form H-bonded donor–acceptor–donor (D–A–D) supramolecular triads TPAD1-PBI-TPAD1 and TPAD2-PBI-TPAD2 with 3,4,9,10-perylene tetra carboxylic diimide derivative (PBI). The presence of multiple H-bonds in the solution state was elucidated by 1H NMR titrations and IR spectral studies. J-aggregations and electron/energy transfers provided by both dendrimers were verified by UV–Vis and photoluminescence (PL) titrations with PBI and the particle sizes of supramolecular triads were calculated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. Similarly, both dendrimers also showed sensitivities towards Cu2+ in comparison with 19 interfering metal ions, which were evidenced via UV–Vis and PL titraions in both single and dual metal systems. The maximum detection limit of Cu2+ ions was determined to be 20 ppm from PL titrations for both dendrimers, and the 1 : 2 stoichiometry of the complexes formed by both dendrimers (TPAD1-Cu2+ and TPAD2-Cu2+) were calculated by Job plots based on UV–Vis absorption titrations. More importantly, the binding mechanism of the 1,3,5-triazine-4,6-diamine probe of both dendrimers was well characterized by 1H and 13C NMR titrations ([D8]THF : D2O = 2 : 1 in vol.) and supported by the fluorescence reversibility by adding metal ions and PMDTA sequentially.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...