Encapsulation of polyphenolic grape seed extract in polymer-coated liposomes†
Abstract
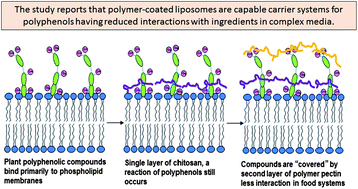
Polyphenolic grape seed extract (0.1 w/v%) was encapsulated in liposomes (1% soy
- This article is part of the themed collection: Delivery of functionality in complex food systems

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...