Nickel(ii) macrocycles: highly efficient electrocatalysts for the selective reduction of CO2 to CO†‡
Abstract
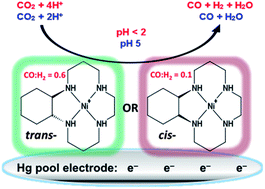
A series of molecular materials that are structurally similar to the NiII macrocycle [Ni(cyclam)]2+ (cyclam = 1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane) have been used as electrocatalysts for the reduction of CO2 at a mercury pool working electrode in aqueous solution. At pH 5, with an applied potential of −0.96 V vs. NHE (overpotential of −0.55 V), the complexes are highly efficient, having both high rate constants and Faradaic efficiencies (F.E.s) for the selective reduction of CO2 to CO. When the pH is below the pKa (pH < 2) of the Ni(H) species (pKas: 0.5–2), the F.E.s are still high but product selectivity changes to yield predominantly H2 from the reduction of water. At least two of the complexes investigated are better electrocatalysts than [Ni(cyclam)]2+, probably due to: (i) surface geometries that are suitable for adsorption onto the mercury electrode surface, and (ii) electronic effects of methyl groups or cyclohexane rings on the cyclam backbone. Mechanistic studies by pulse radiolysis show evidence of Ni(CO2) adducts for two of the catalysts, with KCO2 ∼ 10 M−1 for the reaction of NiI with CO2 in aqueous solution.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Catalysis for Clean Energy

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...