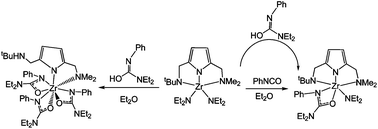
The reactions of Zr(NR2)4 (1, R = Me; 2, R = Et) with an asymmetrical tridentate pincer type pyrrole ligand precursor [C4H2NH(2-CH2NHtBu)(5-CH2NMe2)] and treatment of the derivatives with either PhNCS or PhNCO have been carried out and characterized. Reacting Zr(NR2)4 (1, R = Me; 2, R = Et) with [C4H2NH(2-CH2NHtBu)(5-CH2NMe2)] generates Zr[C4H2N(2-CH2NtBu)(5-CH2NMe2)](NR2)2 (3, R = Me; 4, R = Et) in high yield along with the elimination of 2 equiv of dimethylamine or diethylamine, respectively. Interestingly, while changing the solvent from Et2O to CH2Cl2, the complex Zr[C4H2N(2-CH2NtBu)(5-CH2NMe2)][C4H2N(2-CH2NHtBu)(5-CH2NMe2)]Cl (5) is produced by undergoing C–Cl bond cleavage. Furthermore, reaction of either 3 or 4 with 1 or 2 equiv of PhNCS or PhNCO yields Zr[C4H2N(2-CH2NtBu)(5-CH2NMe2)](NMe2)[PhNC(NMe2)S] (6), Zr[C4H2N(2-CH2NtBu)(5-CH2NMe2)](NEt2)[PhNC(NEt2)O] (7) and Zr[C4H2N(2-CH2NHtBu)(5-CH2NMe2)][PhNC(NEt2)O]3 (8), respectively. All the aforementioned complexes were characterized by 1H and 13C NMR spectrometry and the molecular structures of 5, 6, and 8 have been determined by single-crystal X-ray diffractometry. Complexes 4, 5, and 7 initiated the ethylene polymerization in the presence of MAO as the co-catalyst.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...