Metallomacrocycles as ligands: synthesis and characterisation of aluminium-bridged bisglyoximato complexes of palladium and iron†
Abstract
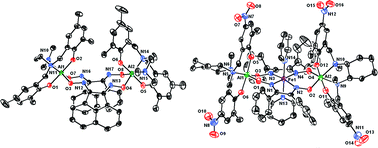
Dialuminiummacrocycles based on bisglyoximato moieties were prepared and their coordination chemistry with FeII and PdII was investigated. The bridging aluminium centers were supported by several types of tetradentate diphenoxide diamine ligands. The nature of the ancillary ligands bound to aluminium was found to affect the overall geometry and symmetry of the metallomacrocycles. Enantiopure, chiral diphenoxide ligands based on the (R,R)-trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane backbone afforded cleanly one metallomacrocycle isomer. The size and electronic properties of remote substituents on aluminium-bound ligands affected the binding mode and electronic properties of the central iron. A structurally characterized iron complex shows trigonal prismatic coordination mode, with phenoxide bridges between iron and aluminium. Increasing the size of the phenoxide substituents led to square bipyramidal coordination at iron. Employing p-NO2- instead of p-tBu-substituted phenoxide as supporting ligands for aluminium caused a 0.27 V positive shift of the FeIII/FeII reduction potential. These results indicate that the present synthetic approach can be applied to a variety of metallomacrocycles based on bisglyoximato motifs to affect the chemistry at the central metal.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent: Americas

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...