Quantifying factors that influence metal ion release in photocaged complexes using ZinCast derivatives†
Abstract
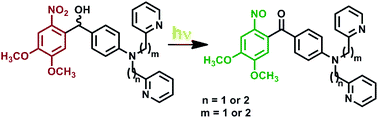
Two generations of nitrobenzhydrol-based photocages for Zn2+ have been prepared and characterized. The first series includes the tridentate ZinCast-1 utilizes a bis-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-aniline ligand that forms a 5,5-chelate ring upon metal binding. The related photocages ZinCast-2 with a N-[2-(pyridine-2-yl)ethyl]-N-(pyridine-2-ylmethyl)aniline (5,6-chelate ring) and ZinCast-3 with a N,N-bis[2-(pyridine-2-yl)ethyl]aniline (6,6-chelate ring) were synthesized for comparative studies. The complexes formed by the ions Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ with three ZinCast and their photoproducts (ZinUnc) were interrogated by UV-Vis spectroscopy. The studies indicate that ZinCast-1 forms complexes of the highest stability and ZinCast-3 exhibits the most significant changes in metal affinity upon uncaging. These results suggest that the changes in nitrogen atom donor ability as well as the initial complex stability must be considered to design a photocage with the desired properties. The composite results were used to design ZinCast-4 and ZinCast-5, the second generation photocages that incorporate an additional adjacent ether ligand into the Zn2+ chelator.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent: Americas

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...