Heterocyclic dithiocarbazate iron chelators: Fe coordination chemistry and biological activity†
Abstract
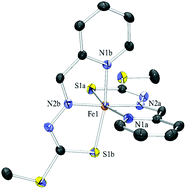
The iron coordination and biological chemistry of a series of heterocyclic dithiocarbazate Schiff base ligands is reported with regard to their activity as Fe chelators for the treatment of Fe overload and also cancer. The ligands are analogous to tridentate heterocyclic hydrazone and thiosemicarbazone chelators we have studied previously which bear NNO and NNS donor sets. The dithiocarbazate Schiff base ligands in this work also are NNS chelators and form stable low spin ferric and ferrous complexes and both have been isolated. In addition an unusual hydroxylated ligand derivative has been identified via an Fe-induced oxidation reaction. X-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic characterisation of these complexes has been carried out and also the electrochemical properties have been investigated. All Fe complexes exhibit totally reversible FeIII/II couples in mixed aqueous solvents at potentials higher than found in analogous thiosemicarbazone Fe complexes. The ability of the dithiocarbazate Schiff base ligands to mobilise Fe from cells and also to prevent Fe uptake from transferrin was examined and all ligands were effective in chelating intracellular Fe relative to known controls such as the clinically important Fe chelator desferrioxamine. The Schiff base ligands derived from 2-pyridinecarbaldehyde were non-toxic to SK-N-MC neuroepithelioma (cancer) cells but those derived from the ketones 2-acetylpyridine and di-2-pyridyl ketone exhibited significant antiproliferative activity.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Application of Inorganic Chemistry for non-Cancer Therapeutics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...