Effects of alkyl chain length and anion size on thermal and structural properties for 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorocomplex salts (CxMImAF6, x = 14, 16 and 18; A = P, As, Sb, Nb and Ta)†
Abstract
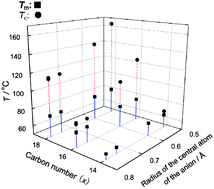
A series of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorocomplex salts (CxMImAF6, x = 14, 16 and 18, A = P, As, Sb, Nb and Ta) have been characterized by thermal analysis, X-ray diffraction and polarized optical microscopy. A liquid crystalline mesophase is observed for all the C16MIm and C18MIm salts. The C14MIm+ cation gives a liquid crystalline mesophase only with PF6−. The temperature range of the liquid crystalline mesophase increases with an increase in alkyl chain length or with decrease in anion size. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction revealed that all the C18MImAF6 salts (A = P, As, Sb, Nb and Ta) are isostructural with each other in the crystalline phase and have a layered structure. The interdigitated alkyl chain of the cation has a bent shape like a spoon near the imidazolium ring in the crystalline phase at −100 °C and is tilted with respect to the sheets of the imidazolium headgroups and anions. An increase of temperature increases the ratio of an all-trans conformation to the bent conformation in the crystalline phase. X-ray diffraction and polarized optical microscopy suggested that the liquid crystalline mesophase has a smectic A2 structure. The interlayer distance increases with a decrease in the anion size since the smaller anion has a stronger coulombic interaction with the imidazolium headgroup, resulting in the decrease of the interdigitated part to give a larger layer spacing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...