Enzyme structure and catalytic properties affected by the surface functional groups of mesoporous silica†
Abstract
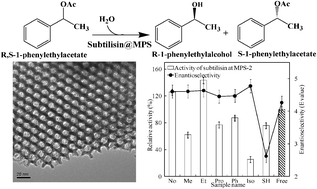
The enzyme subtilisin from Bacillus licheniformis (4.1 nm × 7.8 nm × 3.7 nm) was easily immobilized onto a mesoporous silica (MPS) surface by a direct one-step method and the amount of subtilisin immobilized on each functionalized MPS surface was similar (approximately 0.30 mg of enzyme/mg of MPS support). The catalytic performance (hydrolytic activity and enantioselectivity) of the immobilized subtilisin was found to depend on the properties of the organofunctional group on the MPS surface. In particular, the hydrolytic activity of enzyme immobilized on

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...