On the stabilization mechanisms of organic functional groups on ZnO surfaces
Abstract
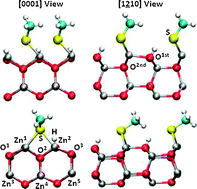
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations have been employed to investigate the interaction between ZnO-(10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) and (1
0) and (1![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 10) surfaces and organic functional groups. We analyze the influence of the surface coverage on the geometries and binding energies under a dry environment. Our calculations show that coverages θ = 1 ML are favored under ligand-rich conditions and a dry environment. However, based on thermodynamic considerations we suggest that these ligands may not be stable against adsorption of liquid water and water vapor.
10) surfaces and organic functional groups. We analyze the influence of the surface coverage on the geometries and binding energies under a dry environment. Our calculations show that coverages θ = 1 ML are favored under ligand-rich conditions and a dry environment. However, based on thermodynamic considerations we suggest that these ligands may not be stable against adsorption of liquid water and water vapor.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...