Dynamics of fluorescence depolarisation in star-shaped oligofluorene-truxene molecules†
Abstract
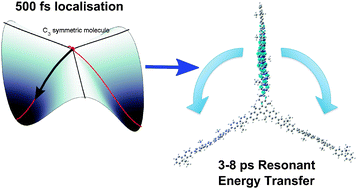
Star-shaped molecules are of growing interest as organic optoelectronic materials. Here a detailed study of their photophysics using fluorescence depolarisation is reported. Fluorescence depolarisation dynamics are studied in branched
- This article is part of the themed collection: Ultrafast chemical dynamics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...