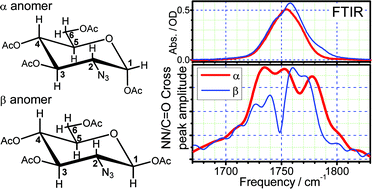
Discrimination between coupling networks of glucopyranosides varying at a single stereocenter using two-dimensional vibrational correlation spectroscopy†
Abstract
A combination of two-dimensional infrared (![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N/C
N/C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretch mode region of the 2DIR correlation
O stretch mode region of the 2DIR correlation ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N stretching mode of the equatorially oriented N3 group with the CO modes when the C1
N stretching mode of the equatorially oriented N3 group with the CO modes when the C1 ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N stretching mode were found to be different for the two anomers; up to a 1.8-fold difference in the energy transport times was observed for the probed modes of the same type in the two anomers. The results demonstrate the capability of
N stretching mode were found to be different for the two anomers; up to a 1.8-fold difference in the energy transport times was observed for the probed modes of the same type in the two anomers. The results demonstrate the capability of
- This article is part of the themed collection: Ultrafast chemical dynamics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...