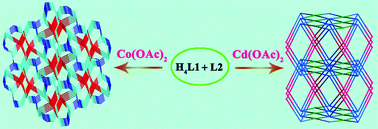
Two novel metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), namely [Co2(L1)(L2)]·4.25H2O (1) and [Cd4(L1)2(L2)2]·4H2O·DMF (2) (H4L1 = tetrakis[4-(carboxyphenyl)-oxamethyl]methane acid and L2 = tetrakis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)methane), have been hydrothermally synthesized. Their structures have been determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analyses and further characterized by infrared spectra (IR), elemental analyses, powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), thermogravimetric (TG) analyses, UV-vis absorption spectra, optical energy gap and emission spectra. In 1, tetrahedral L1 and L2 ligands link neighboring Co(II) atoms to generate a unique 3D self-penetrating framework with a tetranodal 4-connected (6·85)2(63·83)(86) topology. However, in 2, Cd(II) atoms are bridged by L1 and L2 ligands to furnish a 3D framework with a highly rare (4,8)-connected (46)(44·62)(410·614·74) topology. In addition, compound 1 exhibits photocatalytic activity for dye degradation under UV light or visible-light and shows good stability toward photocatalysis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...