Analysis of phenolic acids and their antioxidant activity by capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry with field-amplified sample injection
Abstract
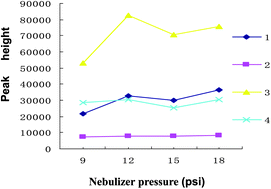
In this study, a capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry (CE-MS) method with field-amplified sample stacking was developed to analyze and detect four hydrophilic active components (danshensu, salvianolic acid B, caffeic acid and lithospermic acid) present in many plant-derived samples, and to evaluate their antioxidant ability. The assay was performed on an uncoated fused-silica capillary of 95 cm × 50 μm I.D. and a positive voltage of 27 kV was applied. The sample was injected under pressure of 50 mbar for 3–300 s and the temperature of capillary was kept 25 °C. Sheath liquid constituted of 5 mM ammonium acetate in methanol solution, flowing at 4 μL min−1, and was supplied to the CE-electrospray interface. The effects of nebulizer gas pressure, the flow rate and temperature of the drying gas, sheath liquid composition and flow rate, and sample injection length were optimized in order to obtain better performance. Utilizing the preconcentration technique, the sensitivity was enhanced by approximately 30–50 fold in terms of limits of detection compared to common hydrodynamic injection without interference from matrix coextractives. The phenolic antioxidant abilities were also determined by simple and accurate free radical spiking test. Furthermore, the method has been successfully applied to a danshen sample.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...