Chromatographic fingerprint of Semen Armeniacae Amarae based on high-performance liquid chromatogram and chemometric methods
Abstract
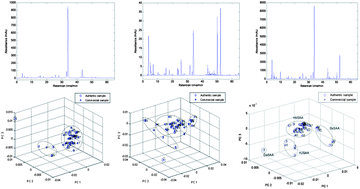
Thirteen real Semen Armeniacae Amarae (SAA) samples and 28 commercial SAA samples were obtained from four typical sources of China. The high-performance liquid chromatographic (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...