Migration behaviour of discontinuous buffers in capillary electrophoresis during protein enrichment†
Abstract
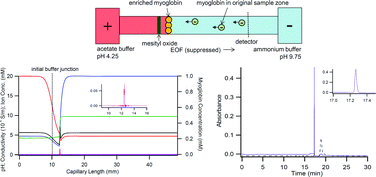
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is not only an effective separation technique, but can also serve as a sample preparation tool for enrichment and purification at sub-microliter sample volumes. Our approach is based on the use of a discontinuous buffer system consisting of an acid and a base (acetate and ammonium). Proteins and/or peptides with isoelectric points between the pH values of these two buffers will become stacked at the neutralization reaction boundary (NRB). To understand the mechanism of the NRB formation and the electrophoretic migration of various ions during the enrichment, we performed experiments using myoglobin and mesityl oxide to reveal the ion migration patterns at the buffer junction, and utilized Simul 5 to computer simulate the process. The simulated results closely resembled the experimental data, and together, they effectively revealed the characteristics of the discontinuous buffers. Importantly, the discovery allowed the manipulation of NRB behaviours by controlling the discontinuous buffer composition. To illustrate this, the removal of urea as an unwanted background molecule from the enriched protein sample was achieved based on the acquired information.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...