Metabolite profiling of Curcuma species grown in different regions using 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis†
Abstract
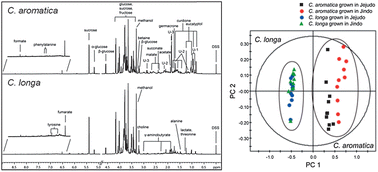
Curcuma is used to treat skin diseases and colic inflammatory disorders, and in insect repellants and antimicrobial and antidiabetic medications. Two Curcuma species (C. aromatica and C. longa) grown in Jeju-do and Jin-do were used in this study. Methanolic extracts were analyzed by 1H NMR spectroscopy, and metabolite profiling coupled with multivariate analysis was applied to characterize the differences between species or origin. PCA analysis showed significantly greater differences between species than origins, and the metabolites responsible for the differences were identified. The concentrations of sugars (glucose, fructose, and sucrose) and essential oils (eucalyptol, curdione, and germacrone) were significantly different between the two species. However, the samples from Jeju-do and Jin-do were different mainly in their concentrations of organic acids (fumarate, succinate, acetate, and formate) and sugars. This study demonstrates that NMR-based metabolomics is an efficient method for fingerprinting and determining differences between Curcuma species or those grown in different regions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...