Using self-driven microswimmers for particle separation†
Abstract
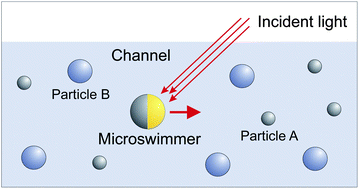
Microscopic self-propelled swimmers capable of autonomous navigation through complex environments provide appealing opportunities for localization, pick-up and delivery of micro and nanoscopic objects. Inspired by motile cells and bacteria, man-made microswimmers have been fabricated, and their motion in patterned surroundings has been experimentally studied. We propose to use self-driven artificial microswimmers for the separation of binary mixtures of colloids. We revealed different regimes of separation, including one with a velocity inversion. Our findings could be of use for various biological and medical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...