Nanoporous core–shell Cu@Cu2O nanocomposites with superior photocatalytic properties towards the degradation of methyl orange
Abstract
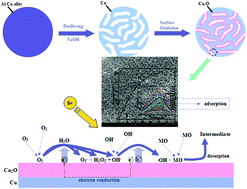
We present a facile two-step strategy to fabricate a novel nanoporous core–shell Cu@Cu2O nanocomposite photocatalyst. The photocatalyst was synthesized via the combination of dealloying of the as-milled Al66.7Cu33.3 (at.%) precursor powders in alkaline media with subsequent surface

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...