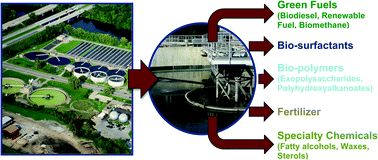
Activated sludge contains a microbial population responsible for the biological treatment of wastewater. This microbial population mostly consists of heterothrophic bacteria which utilize the organic content of the wastewater for growth, either as part of their cellular structures or as energy and carbon storage compounds. These compounds are mostly lipidic in nature and are or could be important raw materials for a multitude of applications in biofuel and oleochemical industries. In this study, a municipal activated sludge was analyzed for lipid storage compounds and other compound classes present in significant concentrations. Three extraction techniques, namely; Bligh & Dyer (applied on dried and partially dewatered samples) and accelerated solvent extractions, were initially investigated to identify the one resulting in the highest gravimetric and biodiesel yields. The highest yields were obtained using the Bligh & Dyer of partially dewatered sludge samples and thus, the extracts from this extraction technique were subjected to a series of analytical procedures such as precipitation, solid phase extraction, thin layer chromatography (TLC), gas chromatography with flame ionization detector (GC-FID) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to characterize the major compound classes present. Results indicated that the major compounds in the samples were polyhydroxyalkanoates, wax esters, steryl esters, triacylglycerides, free fatty acids, free sterols and phospholipids. Hydrocarbons, diacylglycerides and monoacylglycerides were also detected. These compounds are either synthesized by microorganisms or from exogenous contributions. Regardless of the source of these compounds, their persistent presence in activated sludge offers another feedstock for a wide range of applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...