Strategy for catch and release of azide-tagged biomolecules utilizing a photolabile strained alkyne construct†
Abstract
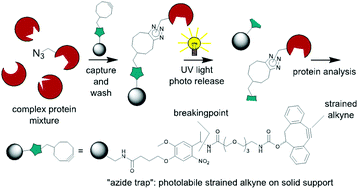
A photolabile o-nitrobenzyl linker–cyclooctyne conjugate was prepared, immobilized on poly(methacrylate) beads and utilized as a trap for azide-functionalized compounds. These could be released by 365 nm UV light irradiation in high yield and purity. The “reagent-free” and time economic catch and release protocol was deemed useful for chemical proteomics applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...