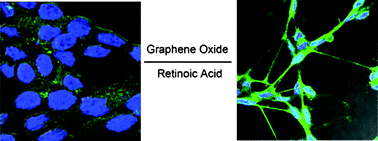
Graphene oxide (GO), has created an unprecedented opportunity for development and application in biology, due to its abundant functional groups and well water solubility. Recently, the potential toxicity of GO in the environment and in humans has garnered more and more attention. In this paper, we systematically studied the cytotoxicity of GO nanosheets via examining the effect of GO on the morphology, viability and differentiation of a human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line, which was an ideal model used to study neuronal disease in vitro. The results suggested that GO had no obvious cytotoxicity at low concentration (<80 μg mL−1) for 96 h, but the viability of cells exhibited dose- and time-dependent decreases at high concentration (≥80 μg mL−1). Moreover, GO did not induce apoptosis. Very interestingly, GO significantly enhanced the differentiation of SH-SY5Y induced-retinoic acid (RA) by evaluating neurite length and the expression of neuronal marker MAP2. These data provide a promising application for neurodegenerative diseases.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...