An integrated fiber-optic microfluidic device for detection of muscular force generation of microscopic nematodes†
Abstract
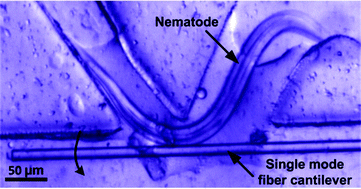
This paper reports development of an integrated fiber-optic microfluidic device for measuring muscular force of small nematode worms with high sensitivity, high data reliability, and simple device structure. A moving nematode worm squeezed through multiple detection points (DPs) created between a thinned single mode fiber (SMF) cantilever and a sine-wave channel with open troughs. The SMF cantilever was deflected by the normal force imposed by the worm, reducing optical coupling from the SMF to a receiving multimode fiber (MMF). Thus, multiple force data could be obtained for the worm–SMF contacts to verify with each other, improving data reliability. A noise equivalent displacement of the SMF cantilever was 0.28 μm and a noise equivalent force of the device was 143 nN. We demonstrated the workability of the device to detect muscular normal forces of the parasitic nematodes Oesophagotomum dentatum L3 larvae on the SMF cantilever. Also, we used this technique to measure force responses of levamisole-sensitive (SENS) and resistant (LERV) O. dentatum isolates in response to different doses of the anthelmintic

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...