Anion photoelectron spectroscopy of germanium and tin clusters containing a transition- or lanthanide-metal atom; MGen− (n = 8–20) and MSnn− (n = 15–17) (M = Sc–V, Y–Nb, and Lu–Ta)†
Abstract
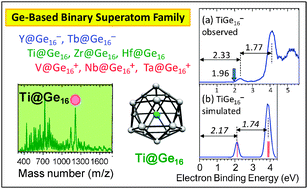
The electronic properties of germanium and tin clusters containing a transition- or lanthanide-metal atom from group 3, 4, or 5, MGen (M = Sc, Ti, V, Y, Zr, Nb, Lu, Hf, and Ta) and MSnn (M = Sc, Ti, Y. Zr, and Hf), were investigated by anion
- This article is part of the themed collection: Structure and reactivity of small particles: from clusters to aerosols

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...