Unravelling the specific site preference in doping of calcium hydroxyapatite with strontium from ab initio investigations and Rietveld analyses
Abstract
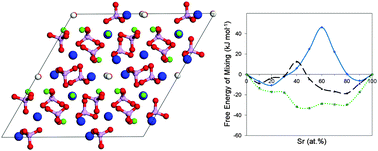
Strontium can be substituted into the calcium sublattice of hydroxyapatite without a solubility limit. However, recent ab initio simulations carried out at 0 K report endothermic nature of this process. There is also striking discrepancy between experimentally observed preference of Sr doping at Ca-II sites and the first principles calculations, which indicate that a Ca-I site is preferred energetically for the Sr substitution. In this paper we combine insights from Density Functional Theory simulations and regular configurational entropy calculations to determine the site preference of Sr doping in the range of 0–100 at% at finite temperatures. In addition, samples of Sr–HA are synthesized and refinement of the relevant structural information provides benchmark information on the experimental unit cell parameters of Sr–HA. We find that the contribution of the entropy of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...