Electrochemical detection for dynamic analyses of a redox component in droplets using a local redox cycling-based electrochemical (LRC-EC) chip device†
Abstract
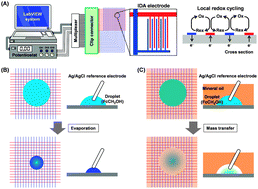
This report describes the electrochemical detection of a redox component in droplets using a local redox cycling-based electrochemical (LRC-EC) chip device consisting of 256 sensors. The time-course analyses showed that the redox compound in the droplet was dynamically changed during droplet

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...