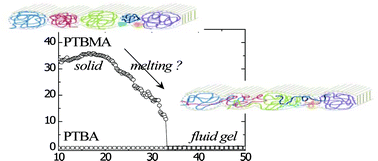
We present an experimental study on the surface rheology of ultrathin films of poly(tert-butylacrylate) (PTBA) and poly(tert-butylmethacrylate) (PTBMA) for which steric hindrance imposed by the methyl group leads to a large intrinsic rigidity of the polymer chain. Whilst PTBA films show weak temperature dependence, PTBMA films undergo a solid–liquid transition at a temperature well below Tg, the glass transition temperature of the bulk polymer. The peculiar behaviour observed for the shear moduli beyond the fluid–solid transition is similar to that observed recently with dispersions of soft colloidal spheres [D. A. Sessoms, et al., Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A, 2009, 367, 5013–5032], where, upon cooling, the system undergoes first a glass transition, followed by a jamming transition. The transition that we observe in PTBMA films could be similar or, alternatively, could be analogous to the glass transition of the bulk polymer.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...