Structural phase transitions and mechanical properties of binary ionic colloidal crystals at interfaces
Abstract
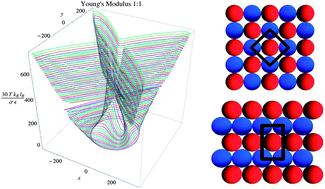
Electrostatic interactions are essential to designing self-assembled structures with unique symmetries and mechanical properties. These interactions can be modified by varying the effective charge of the molecules via the alteration of medium conditions including pH, salt concentration, or dielectric constant variations. In many situations, correlated ionic crystals form at liquid–liquid interfaces, on membrane surfaces, or at solid interfaces that adsorb charged molecules when such medium conditions are modified. In this paper, we determine the structure and mechanical properties, such as the Young's Modulus and Poisson's ratio, of stoichiometric 1 : 1-ionic crystals on surfaces as a function of the medium dielectric constant, which is modified by changing the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...