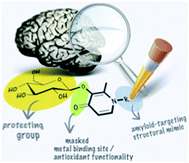
Molecules designed to sequester, redistribute and/or remove metal ions are attractive therapeutic agents in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. The multifactorial nature of the condition and the generally poor target specificity associated with metal ion-binding therapy has led to the development of multifunctional 3-hydroxy-4-(1H)-pyridinone pro-ligands. The excellent qualities of the basic 3-hydroxy-4-pyridinone framework as a low toxicity metal chelator and an antioxidant, as well as its antibacterial and analgesic properties among other functions, inspired us to functionalize it with a framework derived from thioflavin-T, the well-known traditional dye used as a marker to detect amyloid deposits in tissue sections. Thus 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-1-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-4(1H)-pyridinone (HL1), 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-1-(4-methylaminophenyl)-4(1H)-pyridinone (HL2), 1-(4-aminophenyl)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4(1H)-pyridinone (HL3), 1-(6-benzothiazolyl)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4(1H)-pyridinone (HL4), 1-(2-benzothiazolyl)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4(1H)-pyridinone (HL5) and 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-1-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-2-thiazolyl]-4(1H)-pyridinone (HL6) were obtained. Glycosylation, as well as incorporation of structures mimicking those of known amyloid imaging agents, may target drug action to the site of interest, the metal-overloaded amyloid plaques in the Alzheimer's brain. The pro-ligands were assessed for their antioxidant activity, cytotoxicity and ability to interfere with metal ion-induced amyloid peptide aggregation to screen promising lead compounds. Finally, in a brain uptake study with a radiolabeled glucoconjugate pyridinone, 3-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-1-[4-(4-[125I]iodophenyl)-2-thiazolyl]-2-methyl-4(1H)-pyridinone ([125I]-GL7) was shown to cross the blood–brain barrier using an in situ rat brain perfusion technique.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...