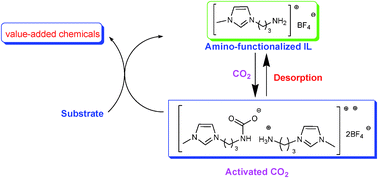
Ionic liquids (ILs), a kind of novel green medium composed entirely of cations and anions, have attracted considerable attention due to their unique properties such as non-volatility, tunable polarity, high stability and so on. In this article, the latest progress on the absorption and subsequent conversion of CO2 by using ILs as absorbents, catalysts or promoters will be summarized. The chemical absorption performance of ILs, especially task-specific ionic liquids (TSILs) such as amino-functionalized ILs, superbase-derived protic ILs has been systematically illustrated. Although significant advances have been made, extensive energy input in the desorption process to recover absorbents would still be a crucial barrier to realizing practical carbon capture and sequestration (CCS). On the other hand, efficient applications of CO2 in the synthesis of valuable compounds such as organic carbonates, urea derivatives, oxazolidinones and formic acid can also be promoted by employing TSILs as catalysts/reaction media. We anticipate that an integration of chemical capture of CO2 with its utilization, a so-called CO2 capture and utilization (CCU) protocol would be an ideal strategy to solve the energy penalty problem in common CCS without the need for additional heat desorption. The essence of this CCU concept is to use TSILs for CO2 capture and substantial activation, which could allow catalytic transformation of CO2 to be accomplished smoothly under low pressure (ideally at 1 atm).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...