Detailed study of the reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization and co-polymerization of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine†
Abstract
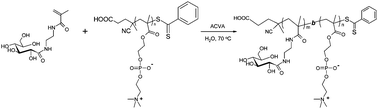
In this paper, we report on a detailed study of the reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT)

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...