Linear dendritic polymeric amphiphiles with intrinsic biocompatibility: synthesis and characterization to fabrication of micelles and honeycomb membranes†‡
Abstract
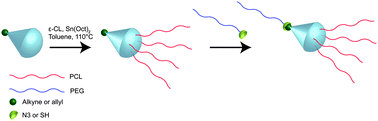
Linear dendritic hybrid materials enable a range of architectural variations which offers novel possibilities in the tailoring of polymeric materials. In this study dendrons based on the 2,2-bis(methylol)propionic acid (bis-MPA) building block, bearing click chemistry moieties in the core and peripheral hydroxyl functionalities, have been used as macroinitiators for ring opening
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...