Are there mechanistic differences between ultraviolet and visible radiation induced skin pigmentation?
Abstract
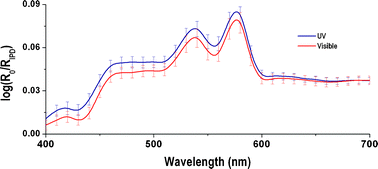
Most of the studies on sunlight-induced pigmentation of skin are mainly focused on ultraviolet (UV) radiation-induced pigmentation and ways to prevent it. Recent studies have shown that the visible component of sunlight can also cause significant skin pigmentation. In the current study, the extent of pigmentation induced by UV and visible regions of sunlight in subjects with Fitzpatrick skin type IV–V was measured and compared with pigmentation induced by total sunlight. The immediate pigment darkening (IPD) induced by the visible fraction of sunlight is not significantly different from that induced by the UV fraction. However, the persistent pigment darkening (PPD) induced by visible fraction of sunlight in significantly lower than that induced by the UV fraction. The dose responses of IPD induced by UV, visible light and total sunlight suggest that both UV and visible light interact with the same precursor although UV is 25 times more efficient in inducing pigmentation per J cm−2 of irradiation compared to visible radiation. The measured diffused reflection

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...