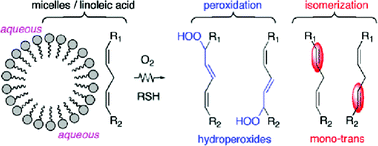
Biomimetic models of free radical-induced transformation of polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as micelles and liposomes, have been used for the study of lipid peroxidation and lipid isomerization. Free radical reactivity of thiol compounds is the common link between the two processes, since lipid peroxidation is inhibited by thiols, due to their H-donation ability, whereas lipid isomerization is catalysed by S-centered radicals. In this paper the two processes are compared for the first time, in solution and under biomimetic conditions, demonstrating that hydroperoxides and trans lipids are formed to comparable extents as a result of oxidative free radical conditions. The biomimetic model of micelles of linoleic acid, prepared by addition of a non-ionic surfactant (TWEEN®-20) and 2-mercaptoethanol as the amphiphilic thiol, was irradiated by ionizing radiation up to 400 Gy under various conditions. In air-equilibrated solutions, the cis–trans isomerization process was observed with a catalytic cycle of 370 together with a substantial amount of hydroperoxides (LOOH). The effect of micelle size was also studied in order to envisage the effect of the supramolecular organization on the outcome of the two processes, and in particular, for the positional preference of the double bond isomerization.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...