Electrospray mass spectrometry for detailed mechanistic studies of a complex organocatalyzed triple cascade reaction
Abstract
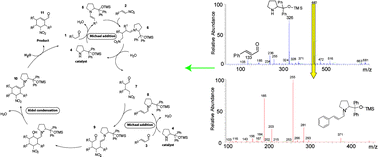
The development of modular combinations of organocatalytic reactions into cascades has been shown to be an effective tool despite the fact that the mechanism of such a complex organocatalytic multistep cascade reaction still remains poorly understood. Here the detailed mechanistic studies of a complex organocatalytic triple cascade reaction for the synthesis of tetra-substituted cyclohexene carbaldehydes are reported. The investigation has been carried out using a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...