Chemometric modeling and pharmacophore mapping in coronary heart disease: 2-arylbenzoxazoles as cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors†
Abstract
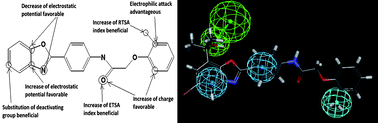
The plasma concentration of HDL-C and the prevalence of coronary heart disease (CHD) is inversely related. Inhibition of cholesteryl ester transfer

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...