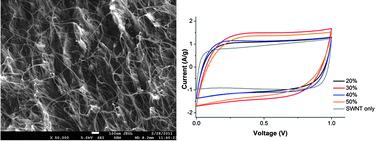
Supercapacitors are promising energy storage and power output technologies due to their improved energy density, rapid charge-discharge cycle, high cycle efficiency and long cycle life. Free standing poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) poly(styrene sulfonate)/single walled nanotube films have been characterised by scanning electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy and thermo-gravimetric analysis to understand the physical properties of the films. Films with varying compositions of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(styrene sulfonate) and single walled nanotubes were compared by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge/discharge to understand their electrochemical properties. A comparison of the results shows that having single walled nanotubes dispersed throughout the polymer matrix increase the capacitance by 65% and the energy density by a factor of 3 whilst achieving good capacity retention over 1000 cycles.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...