Transformation of hydrophobic iron oxide nanoparticles to hydrophilic and biocompatible maghemite nanocrystals for use as highly efficient MRI contrast agent†
Abstract
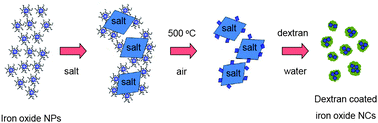
We report a transformation of hydrophobic
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Transformations of Nanoparticles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...