Functionalisation of recombinant spider silk with conjugated polyelectrolytes
Abstract
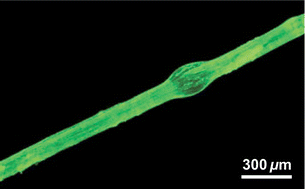
Conjugated polyelectrolytes are demonstrated to permit facile staining of recombinant spider silk fibres. We find that the polyelectrolyte concentration and pH of the staining solution as well as the incubation temperature strongly influence the efficiency of this self-assembly process, which appears to be principally mediated through favourable electrostatic interactions. Thus, depending on the choice of staining conditions as well as the polyelectrolyte, electrically conductive or photoluminescent recombinant silk fibres could be produced. In addition, staining of natural Bombyx mori silk is established, which emphasises the versatility of the here advanced approach to functionalise silk-based materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...