Fluid-shear-stress-induced translocation of aquaporin-2 and reorganization of actin cytoskeleton in renal tubular epithelial cells
Abstract
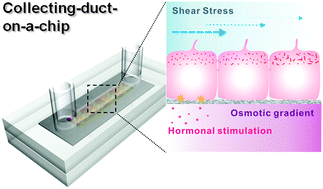
In vivo, renal tubular
* Corresponding authors
a
Interdisciplinary Program in Nano-Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea
E-mail:
sky4u@snu.ac.kr
b School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea
c Interdisciplinary Program of Bioengineering, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea
d
Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Taegu 700-422, Korea
E-mail:
thkwon@knu.ac.kr
In vivo, renal tubular

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
