Road traffic noise: self-reported noise annoyance versus GIS modelled road traffic noise exposure
Abstract
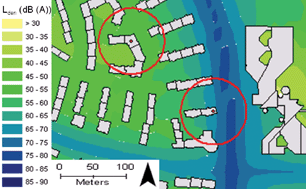
Background and objectives: self-reported road traffic noise annoyance is commonly used in epidemiological studies for assessment of potential health effects. Alternatively, some studies have used geographic information system (GIS) modelled exposure to road traffic noise as an objective parameter. The aim of this study was to analyse the association between noise exposure due to neighbouring road traffic and the noise annoyance of adults, taking other determinants into consideration. Methods: parents of 951 Munich children from the two German birth cohorts GINIplus and LISAplus reported their annoyance due to road traffic noise at home. GIS modelled road traffic noise exposure (Lden, maximum within a 50 m

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...